|
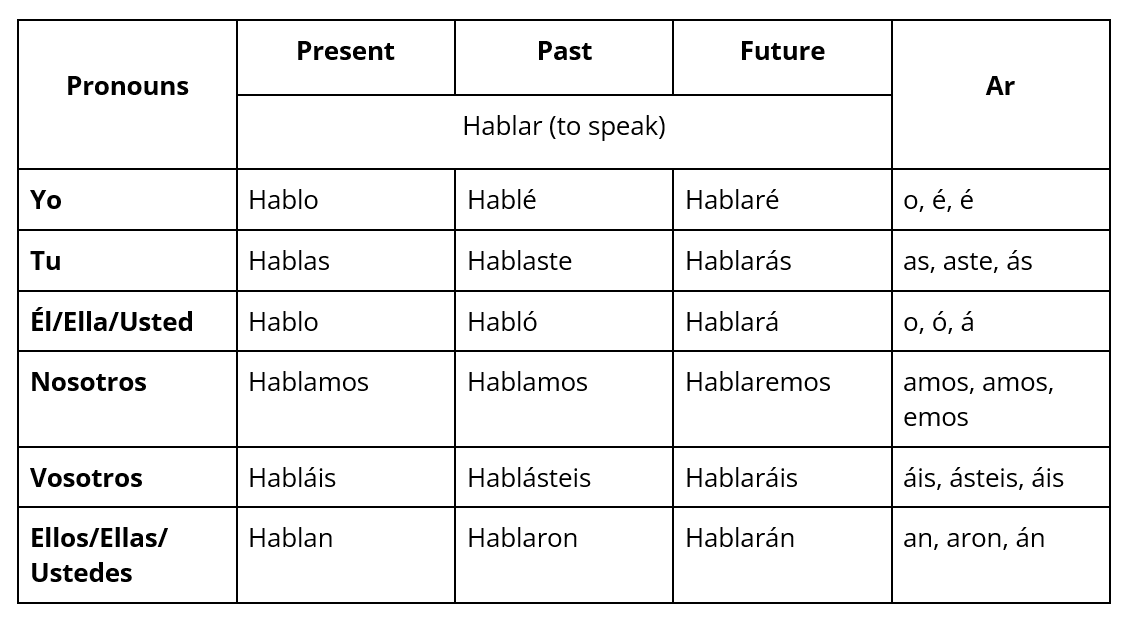
Are you having a difficult time learning Spanish grammar? We’ll break it down for you in this week’s blog. Grammar is the system of rules and structures that govern a language. In summary, Sandy Chung and Geoff Pullum state that grammar includes word order, verb conjugation, and sentence formation to build syntax. It helps establish semantics, which pertains to the meaning of words and sentences within a language and how context influences interpretation. Additionally, it dictates phonetics and phonology, which are related to how words are spoken and written. Whether you're a beginner or an intermediate learner, mastering the essential grammar rules is crucial for effective communication. The following key grammar tips will help you start and become proficient in Spanish. 1. Understand Verb Conjugation in Spanish Verbs in Spanish undergo changes in their forms based on the subject and tense. There are two forms of verbs: regular verbs, which adhere to specific spelling patterns, and irregular verbs, which alter their structure with each conjugation. For instance, "Bailar" (to dance) is a regular verb: yo bailo (I dance), tú bailas (you dance), nosotros bailamos (we dance). In contrast, "Querer" (to want) is irregular: yo quiero (I want), tú quieres (you want), nosotros queremos (we want). Spanish verbs can be classified into three primary verb conjugations: -ar verbs, -er verbs, and -ir. However, each verb’s conjugation varies depending on the tense, which signifies the time frame of a situation and its corresponding form. Let's examine a regular verb and observe its conjugation pattern in the past, present, and future tenses: The selection of verb conjugation hinges upon both the addressee and the intended message. Various verb endings, such as -er and -ir, align with specific grammatical constructions. Furthermore, irregular verbs like ser (to be), ir (to go), decir (to say), and others demand special consideration attention as they deviate from the standard conjugation patterns of regular verbs.
2. Ser vs. Estar In Spanish, two verbs can be translated as "to be": ser and estar. Ser describes inherent or permanent characteristics, such as nationality, professions, or physical attributes. It answers the question, "What is it?" For example, "Soy profesor" means "I am a teacher." Being a professional is considered something permanent or inherent. Estar describes temporary states, locations, feelings, or conditions. It answers the question, "How is it?" For example, "Estoy cansado" means "I am tired." Being tired is a temporary state or condition. 3. Gender Spanish nouns have genders (masculine and feminine). It's essential to know the gender of nouns because adjectives, articles, and even pronouns must agree in gender and number with the nouns they modify. Let’s see some examples: Masculine: El gato es bonito (The cat is handsome); Los gatos son bonitos (Cats are handsome). Feminine: La gata es bonita (The cat is pretty); Las gatas son bonitas (Cats are pretty). While many nouns follow a pattern where those ending in -o are often masculine, and those ending in -a are often feminine, it's important to note that there are exceptions to this rule. Some nouns do not follow these gender-based endings, and their gender must be memorized. 4. Pronoun Usage Pronouns are essential to any language, and Spanish is no exception. While English has only one word for "you" (regardless of formality or number), Spanish has different pronouns for each situation, depending on the context and the level of formality required. For example:
5. Subjunctive Mood The subjunctive mood expresses desires, doubts, wishes, emotions, and uncertainty. It is essential for expressing opinions and hypothetical situations. Common triggers for the subjunctive mood include phrases like "quiero que" (I want that), "es posible que" (it's possible that), and "dudo que" (I doubt that). To use the subjunctive correctly, you'll need to become familiar with its triggers, such as verbs of influence (querer, desear), expressions of doubt (dudar, no creer), and impersonal expressions (es necesario que, es importante que) because it’s used in various tenses, and its conjugation depends on the verb's root and the subject. 6. Prepositions Prepositions are words that indicate relationships between different elements in a sentence. They can be tricky because they don't always translate directly from English. Here are some common Spanish prepositions along with their English translations: "a" - to, at "de" - of, from, "con" - with, "por" - for, by, "para" - for, to. It's important for learners to understand how these prepositions are used in context, as their usage can vary from what might be expected based on direct word-for-word translations. 7. Accent Marks Spanish uses accent marks to indicate the stress or emphasis in a word, and they play a crucial role in the language. Correct accent placement is important because it can alter the meaning and pronunciation of words. Common rules for accent marks in Spanish include:
Follow these 3 ways to improve faster! 1. Study Plan:
2. Learn in Context
3. Practice Every Day
To delve deeper into this topic and enhance your understanding, we invite you to schedule a free consultation with us today!
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
AuthorWrite something about yourself. No need to be fancy, just an overview. Archives
June 2024
Categories
All
|
Music & Language Learning Center |
Music Classes |
Language Classes |
MUSIC AND LANGUAGE LEARNING CENTER 2024



 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

